How does this work in detail?
Purchasing optimization
Current process
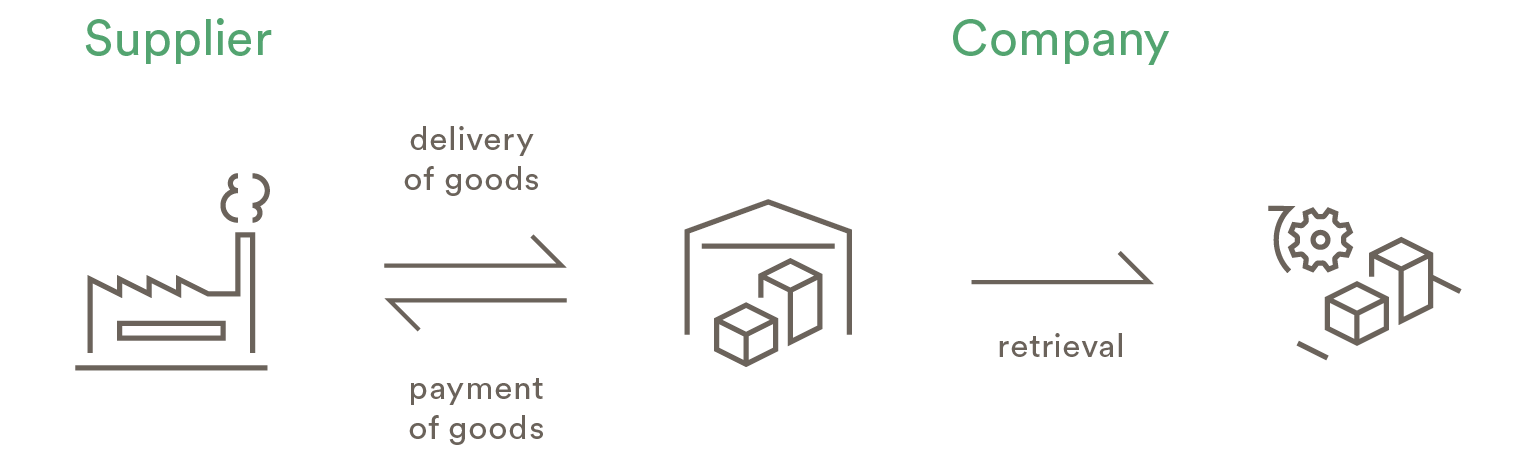
The supplier delivers the ordered goods to the company’s warehouse. At the time of production the goods are called off. The company pays the supplier on the due date (usually between 30 and 60 days after delivery).
New process

The supplier delivers the ordered goods to jtw’s warehouse. At the time of production the company calls the goods that will be transferred to the company. jtw pays the supplier within the agreed discount period. The company pays jtw at the due date (extension up to 120 days and more possible).
How does the purchasing optimization work:
- before
- after
Shortening of
the balance sheet
The goods are taken on the balance sheet of jtw at the time of delivery. This reduces the company’s balance sheet by the value of the goods for the time of storage.
Stabilisation of
the supply chain
jtw pays the supplier taking advantages of the agreed early payment discounts while complying with the payment provisions. This increases the supplier´s liquidity and strengthens the relationship between the supplier and the company.
Strengthening of
the liquidity
jtw agrees with the company on a payment term that is significantly longer than the one agreed with the supplier. The longer payment term and the later invoicing (after delivery of goods to the company) shortens the cash-2-cash cycle (C2C), which increases liquidity of the company.
Reduction of
the debt capital
The improved liquidity can be used to finance growth or for planned operating investments without debt capital is being required for this purpose.
Optimization of
the balance sheet ratios
The reduction in inventories in conjunction with the expansion of payment terms improves the key figures DIO, DPO and C2C as well as the debt ratio.
Improvement of
the credit rating
The reduction in inventories in conjunction with the expansion of payment terms improves the key figures DIO, DPO and C2C as well as the debt ratio.

